Abstract reasoning is a common component of police entry tests. If you’re preparing for a police exam or entrance assessment, you’ll need to understand the different types of abstract reasoning questions and what the objectives are.
Make no mistake, abstract reasoning is challenging, and for some applicants, they find it very frustrating, partly because there is really no step by step process to follow, there’s no formula that you can apply like you might be able to do in numeracy skills for example. Three is certainly effective strategies to help you answer the questions though.
Abstract reasoning is very visual. You won’t have worded questions, there won’t be numbers in the question, instead, the questions are presented visually as images and patterns, and we need to problem solve by analysing these patterns.
Which States/Territories Test Police Applicants For Abstract Reasoning Ability?
- Victoria Police
- Queensland Police Service
- Australian Federal Police
- Western Australia Police
There are typically five different types, or styles, of abstract reasoning questions.
- next in sequence
- most like
- odd one out
- relationship box
- find the middle
Let’s go through some examples and we’ll take a closer look at the types of questions that are in each of those different styles of abstract reasoning questions.
Next in Sequence Questions
Okay, so the first type is next in sequence.
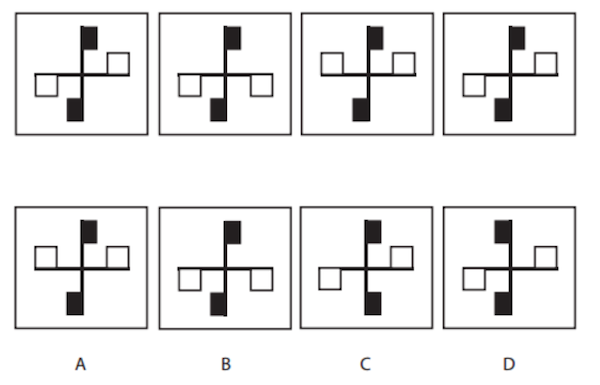
What happens here is we’re looking for a pattern, and we want to find what the next logical option might be to continue that pattern or sequence. So let’s have a look at a couple of examples. So we’re looking at the shapes in the top row, and we need to determine which option from the bottom row best continues the pattern or sequence that appears in the top row.
In the example above, we’ve got four different boxes and there are different colours (black and white) and different shapes involved. And again, we need to determine what pattern is happening so that we can select the appropriate option from the bottom row.
So here’s another example, in a slightly different format.
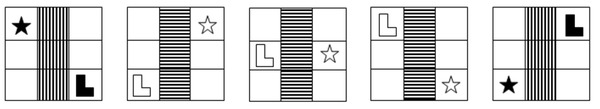
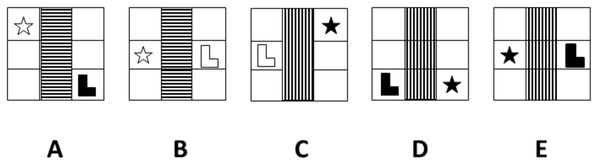
There are five boxes here in the top row, and five options from the bottom row to select. But the same objective applies to this question here, which option from the bottom row best continues the pattern or the sequence that you detect from the top row.
Here’s another example, slightly different in style, but again, we’re looking for the option for the bottom row, A, B, C, D, or E, that would naturally continue the sequence or pattern that we see in the top row.
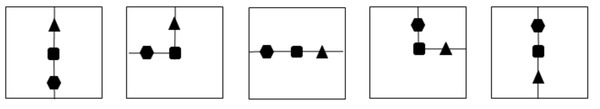
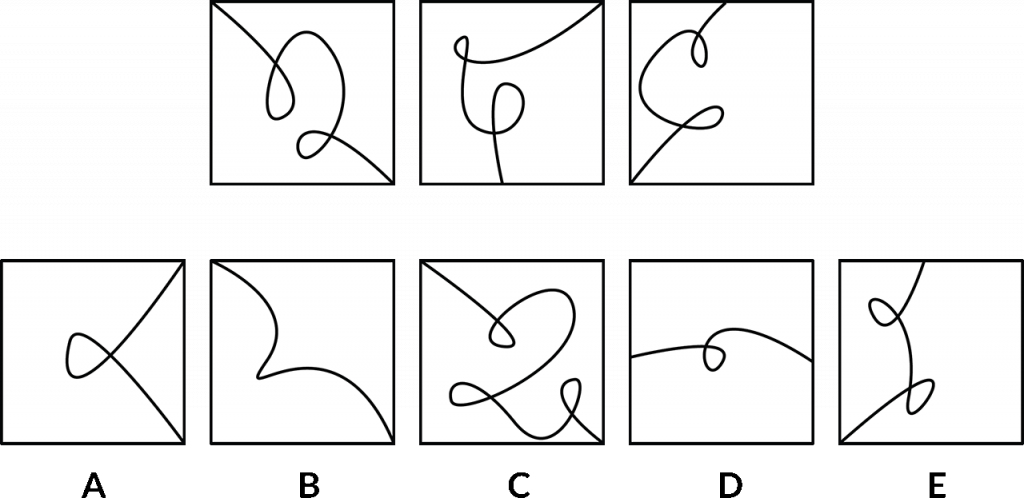
How to solve a next in sequence abstract reasoning question – example demonstration
Most Like Questions
Okay, so that was the next in sequence. Let’s look at the next type, which is most like.
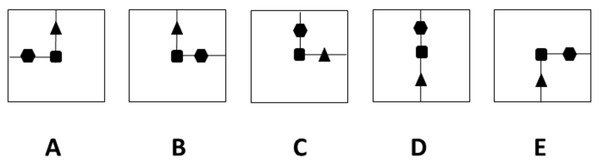
So we’re looking for an option that matches the examples shown. So let’s have a look at an example to start us off. The question is which option from the bottom is most like the images in the top row? There’s something going on in those top three squares, and one of the options below matches what’s going on in those top three. Okay, so we’re looking for the one that’s the same.
Let’s go on to the next one.
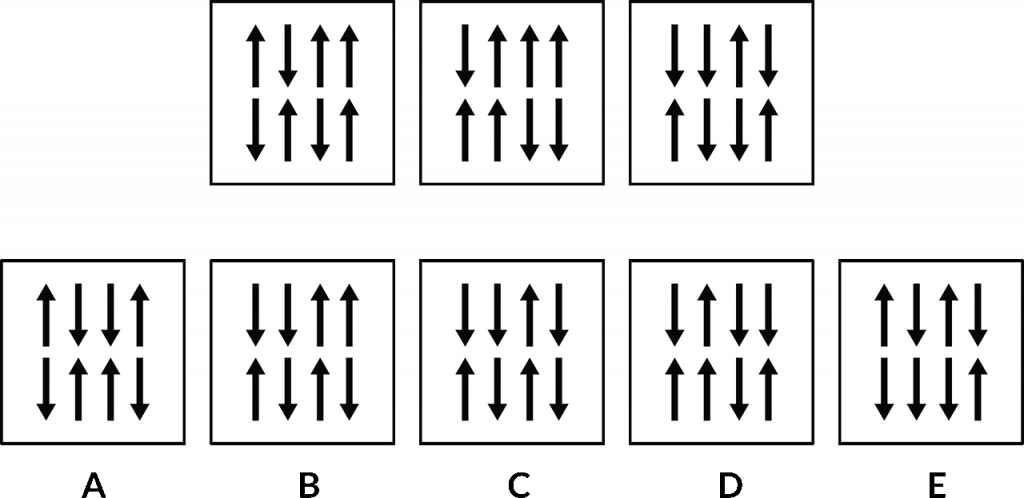
Which option from the bottom is most like the images in the top row? So three options in the top row, different shapes, different patterns, but there’s something unique about them that binds them together. And there’s something about one of the options below, A, B, C, D, or E, that has the same rule or matches the top row for some reason.
That’s what we’re looking for, what is it about the top row that brings them together so that I can select from the bottom row?
Let’s look at one more example.
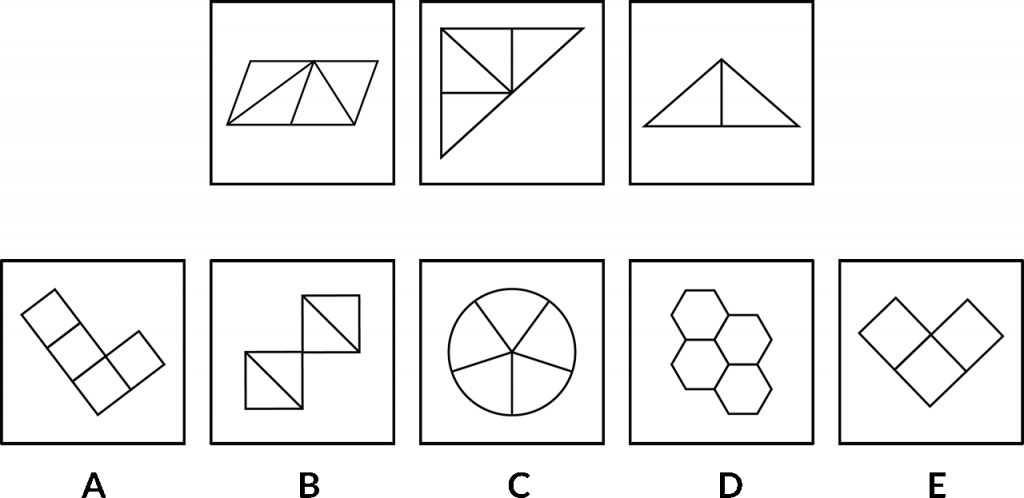
The same objective applies here, we need to choose from the bottom row here to identify which one of those most matches the three in the top row.
What is it about the top three that bring them together or make them similar so that we can identify which one in the bottom row has that same rule or that same condition?
Odd One Out Questions
Alright, and the next type of abstract reasoning question is to identify which one of the items presented is the odd one out for some reason. So let’s take a look at an example here.
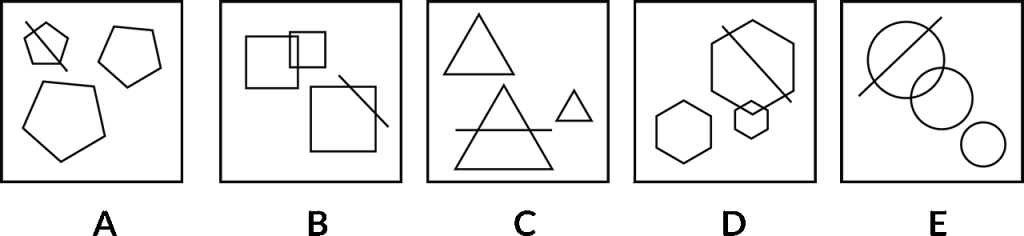
So, which image is the odd one out? There’s something about the images here that again, binds them together or makes them similar for some reason. One of these options doesn’t meet that criterion and we need to identify that.
Let’s look at the next example.
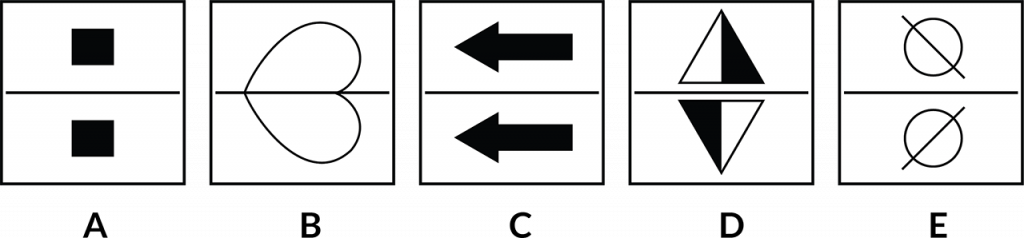
This one’s a little different to the one that we just looked at. There’s a different principle going on here, but the objective is the same. We need to identify which of these options is the odd one out. For some reason, it’s not like the other ones and it doesn’t fit.
Alright, let’s look at one more.
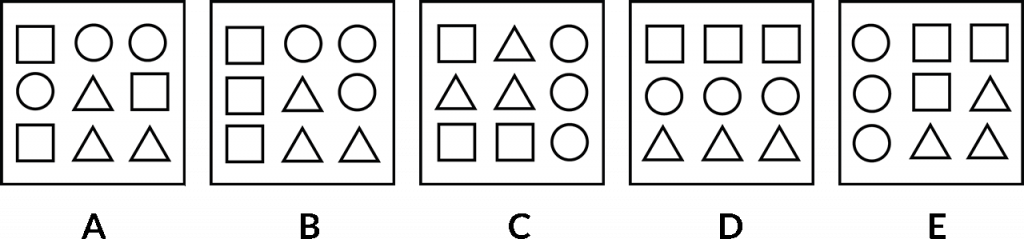
The same question, which is the odd one out? So again, there’s something about these options here, or these images presented that are alike in some way, but one of them doesn’t fit that. Now there’s a lot going on in this particular example, it could simply be that it’s a number of a certain shape that is the same across four of these images, but isn’t the same with the fifth image.
So for example, it might be the number of triangles or the number of circles, or it could be the position of those shapes within the larger box. But either way, we need to try to identify what’s similar about these ones to help us identify the one that might be the odd one out.
Relationship Box Questions
Okay, let’s move on to the next type of abstract reasoning question, which is relationships. Let’s jump into an example.
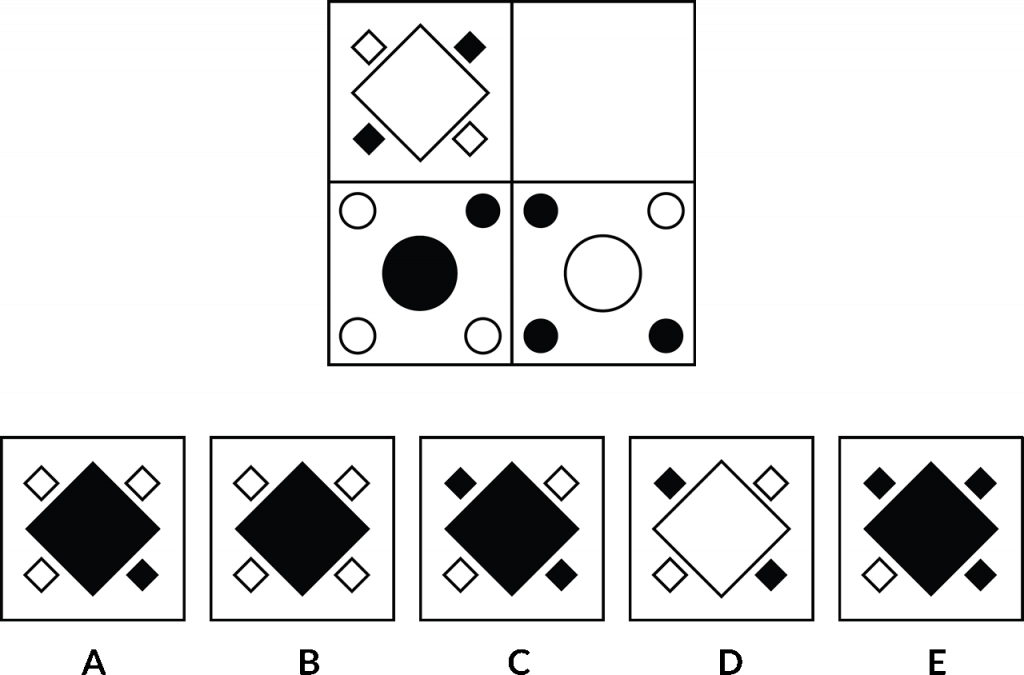
You can see down the bottom, A, B, C, D, E are the options to choose from, and one of those will fit into the blank square in the top right corner of this grid. Now in the bottom section of the grid, you’ll see these circles with the black and white colours there.
There’s some type of relationship or connection be between those two. Now a similar relationship or connection exists between the squares in the top part of this grid, and one of the options below, A through to E. We need to find the relationship that’s going on in the bottom part of the grid to help us identify which option goes in the top part of the grid in that blank space there. Not easy, these ones!
You have to be really flexible in the way that you look at these because the relationship that’s going on can vary from question to question.
Okay, let’s go on to another example.
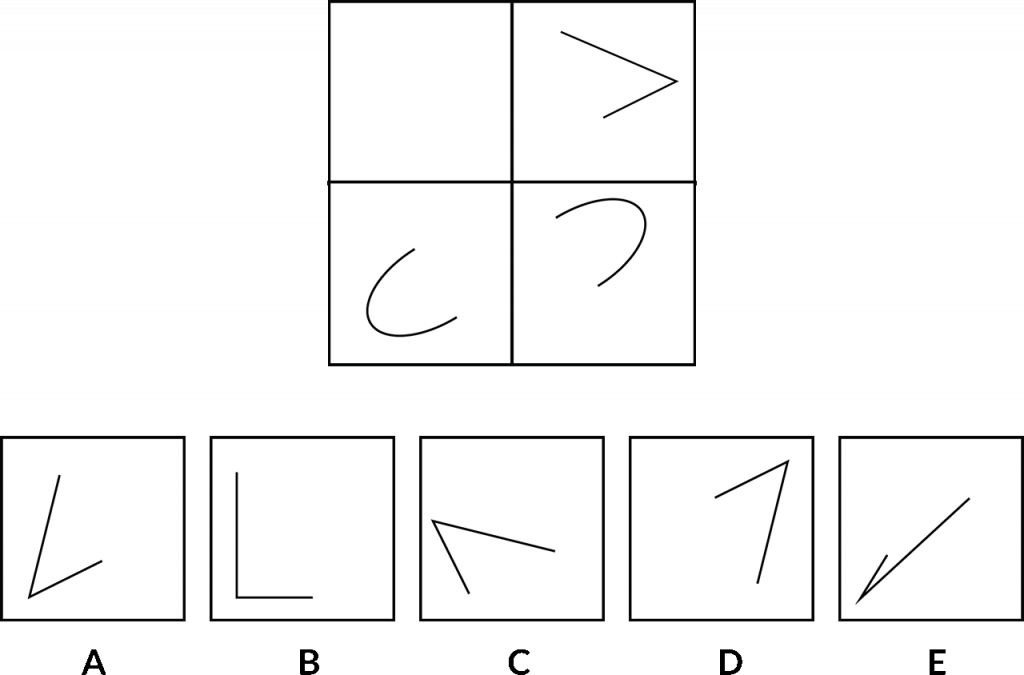
We’re looking to identify the relationship between the items in the bottom section of the grid to help us identify which of the options below, A, B, C, D, or E, has the same relationship to the shape in the top part of the grid, right? These are pretty challenging, these ones. So again, keep a really open mind about what that relationship might be.
Okay, let’s look at one more example of a relationship abstract reasoning question.
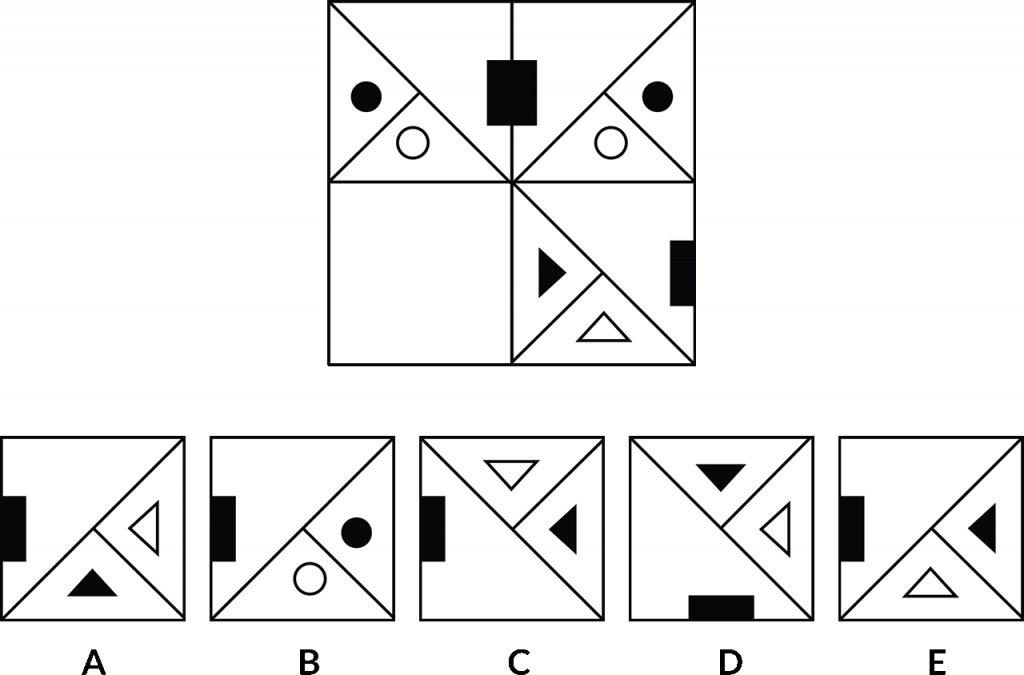
The same objective here. We need to select A, B, C, or D to place into the blank space within the grid. We can see that the blank space has moved around and it could appear in any one of those four places. So now, of course, we really need to focus on the top part of the grid.
What is it between those two images that in some way join them, connects them, or there’s a relationship of some type that exists there. The same type of connection or relationship exists between one of the bottom options and the image that we can see in the bottom part of the grid.
Find The Middle Questions
All right, so I hope you’re going okay with those. Let’s move on to the next type, which is to find the middle position.
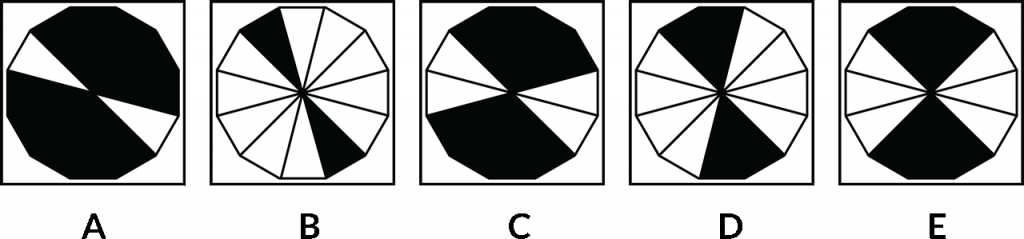
So what we need to do here is to actually sort these five images into what would be a logical order first, before we identify which one would actually then find itself in the middle position. Okay, so as the question says here, place these boxes in a logical order. Okay, now we need to determine which option is in the middle position. So here we’re going A, B, C, D, E, but that may not be the logical order when you’re looking at these images.
Now it could be that something is increasing from 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or it could be going backwards from 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, something might be rotating clockwise one step each time, it could rotate anti-clockwise. There are a number of things that could be happening, but we need to identify what that is so that we can first place these boxes into a logical sequence.
Once we’ve done that, we’ll be able to identify which of the letters would actually finish in the middle position. So it could be that E or B end up in the middle position. It’s not necessarily the correct order to start with. In fact, usually, it’s not the correct order because that’s the first part of the objective is to put them in order to determine which one would then fall into the middle position.
Okay, so that’s probably explained that, I think let’s move on to another example.
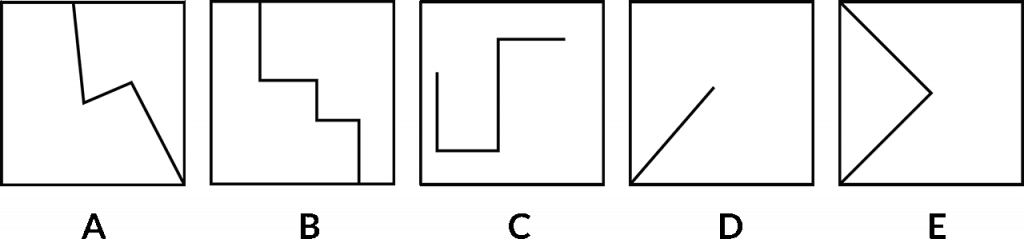
Again, the same thing. We need to place them in a logical sequence and then determine which one would then fall into the middle position.
Our lucky last example.
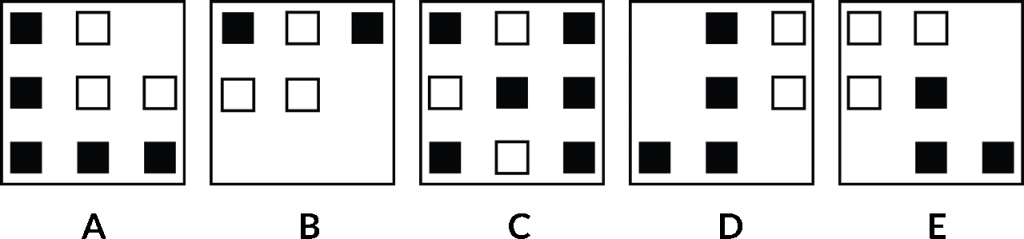
The same thing going on here, different colours, different numbers of squares. There might be different shapes that could be rotating. Something could be added, something could be taken away, lots of possibilities. But the objective of this type of abstract reasoning is to sort them in a logical seek and then determine which one falls in the middle position.
As you can see, abstract reasoning questions can be challenging. If you’re preparing for your police entrance exam you should spend some time developing your understanding of the “rules” of abstract reasoning and doing a heap of practice questions. We can certainly help you with this if you need us.
How To Prepare For Your Abstract Reasoning Police Exam
A combination of elements is necessary to improve your ability to deal with these types of questions in your police exam, especially given the strict time limit for this test.
- Understand the “rules” of abstract reasoning
- Work through a lot of practice questions explanations
- Do plenty of practice tests
These are all components covered in our Entrance Exam Course.



